Our Services
Brightside Solar offers full-service solutions to meet your specific residential or commercial solar needs.
Contrary to widespread belief, solar panels do not have to occupy huge amounts of space, whether on a roof or on land.
Our goal is to make your switch to solar effortless, whether your energy needs are small or large.
Grid-Tie
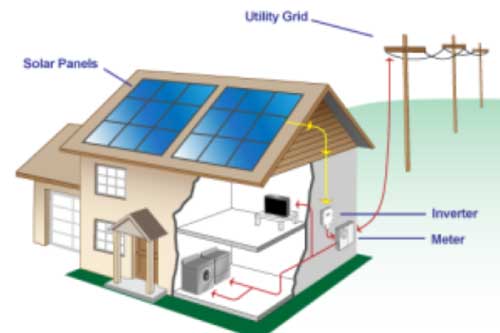
Solar panels generate electricity during the day for use in a home. When the PV system is producing more power than is being consumed by a home or business, excess power is fed into the utility grid and the meter spins backwards. Any surplus produced during a billing period may be credited to the following billing period. Spinning the meter backwards and accruing “banked power” to be used by a home during times when solar is not available, such as at night, is commonly referred to as “net-metering”.
Typical grid-tie system components include the following:
- Solar panel array
- Inverter to convert DC power into AC power
- Circuit protection and utility disconnect switch
Grid-Tie with Battery Backup
Grid-tied systems with battery back-up do however cost more than straight grid-tied systems (up to 40% more expensive based on some estimates). The added expense results from additional components (i.e. batteries and charge controllers). However, proper battery maintenance and charging can reduce costs by extending battery bank shelf life up to ten years. Photovoltaic electricity is used to charge a backup battery bank as well as power household loads. When the battery bank is full, excess PV energy is sold back to the utility grid. During utility power failures, battery backup can power critical loads such as lighting, pumps for heating systems, and communications.
Typical grid-tie with battery backup system components include:
- Solar panel array
- Inverter
- Circuit protection and utility disconnect switch
- Battery charge controller
- Small battery bank and protective encasement
Solar Basics…

SOLAR ARRAYS

INVERTERS
As the solar array generates an electrical current, the energy flows through a series of wires and conduit to an inverter. The inverter’s function is to turn the electricity from the DC format generated by the solar array to the AC format that is commonly used by a home or business. The inverter is typically located in an accessible location usually located on a wall near your main service panel. In most cases, Inverters have displays that allows you to read data about how your solar energy production and are usually connected to the internet to allow you and Brightside Solar to monitor your system’s performance remotely.

SERVICE PANEL

SOLAR NET METER

SYSTEM MONITORING
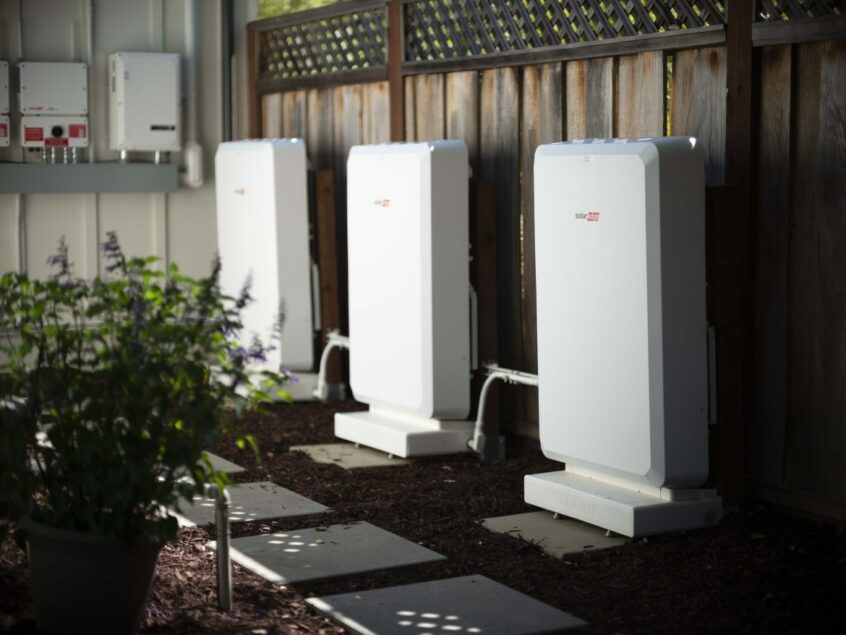

BATTERY STORAGE
The market for home energy storage options like the Sonnen Batterie has taken off in recent years, and costs are falling quickly. Many homeowners and businesses are thinking about adding a battery backup to their solar panel system. A battery storage system can allow you to stay powered up for as long as the utility is down. Brightside Solar is a certified installer for Sonnen Batterie and with their battery back-up system can provide peace of mind by delivering a clean, reliable, and noiseless way to keep the lights on during power outages. Batteries that are recharged by your home’s solar PV system can also allow you to save money in the future should rate structures change with the local utility.

